It’s been almost two years since the launch of the Google AMP Project. Its aim from the start was to help foster better web standards, which could result in an improved mobile experience for users. Now, the project is turning a new leaf and expanding towards email, which brings us to how this shift might affect you.
AMP for email is still in development and we don’t know what the finished product will look like yet. However, what we do know enables us to paint a decent picture of how the project could affect email marketing. In this article, we’ll discuss how the AMP Project has evolved since its creation and what it means for email. We’ll then talk about how you can prepare for the launch of AMP for email. We’ve got a lot of ground to cover, so let’s get to it!
An Update on the Google AMP Project
Google AMP launched in 2016 to some controversy, but the project is still moving along.
We talked about the AMP Project shortly after it launched in 2016, including some instructions on how to integrate it with WordPress. In case you need a refresher, the project is an initiative meant to improve the overall performance of the mobile web. To do that, it aimed to foster a lightweight framework that would result in faster-loading websites.
Since those early days, over 25 million domains have launched AMP content. Furthermore, Google wants to convince the group in charge of web standards to adopt technologies similar to AMP. In the meantime, they’ve also been busy with the launch of AMP stories and the development of AMP for email.
However, while AMP development forges ahead, there are a lot of people worried about what it means for the future of the web. Some are concerned that Google wants to favor AMP articles. Since this content is only accessible through Google’s applications, it mostly benefits the people that choose to adapt to the company’s guidelines.
Additionally, some people argue it stands in contrasts with the ideals of an open web. Others have gone on to suggest some changes AMP could adopt, so it doesn’t favor Google’s ecosystem. For now, the discussion continues, and Google’s AMP for email project only gives us more food for thought.
What AMP for Email Is

Just as its parent project, AMP for email has also stirred passions since its announcement.
AMP is nothing if not ambitious, and now the project wants to tackle another critical aspect of the web – email. The goal of AMP for email is to provide you with the tools to create more engaging and actionable messages. For example, when you open an AMP-enabled email, you’ll be able to complete specific tasks without opening a website. Those include RSVPs, scheduling appointments, or even running simple applications.
Another feature that AMP for email promises is the ability to include self-updating information within messages. For example, you could book a flight and your confirmation email would always include relevant up-to-date information, such as warnings about delays. This would also enable you to send promotional emails that update to reflect when the sale is over, to avoid confusion.
So far, AMP for email is still in its beta phase. You can gain access to it through the Gmail Developer Preview of AMP for Email program if you want to test it in advance. Some companies, such as Pinterest and Booking.com, are already working on how to use AMP for email to their advantage. However, as great as the project’s new features sound, not all people are as excited about it.
A recent Techcrunch article argues that email’s main selling point is its simplicity. If you take email and add new features to it, you’re going to run into interoperability issues. This is a valid point since AMP for email is set to launch later this year, only for Gmail users. It’ll be up to other clients and providers to decide if they want to support AMP emails, which is bound to complicate things somewhat.
Another potential downside of the AMP for email project is it extends Google’s control over the content you see even further. For example, without AMP emails, you’d be forced to open a new page if you wanted to RSVP to an event or schedule an appointment. Now, a lot of people won’t need to leave Google’s email ecosystem to do that, just like with AMP pages. Couple that with the fact that Gmail is one of the leading email platforms and these drastic changes become even more troublesome.
Finally, there’s also the glaring issue that performance isn’t such a big deal when it comes to email versus websites. In most cases, the emails we get don’t take that long to load by design, as most providers have a maximum size limit. That means AMP for email’s primary goal is not performance oriented but adding new features to a medium that already works. In fact, adding all that new functionality to emails may end up slowing their performance. However since the project is still in development, it may not be time to panic just yet. Instead, what you can do is consider how it’ll affect you.
How to Prepare Your Campaigns for AMP for Email
There are two ways you can go about testing AMP for email in its current version. If you’re a developer, you can apply to Gmail Developer Preview of AMP for Email program. You will need to sign a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) if you get in, so keep that in mind:
However, since AMP is an open source, you can also review its specs by checking out the project’s repository. The difference, in this case, is you won’t be able to test the code using a beta version of Gmail, as you would signing up for Google’s developer preview. So far, you can check out AMP for email’s proposed design:
<!doctype html>
<html amp4email> <!-- `amp4email` also accepted. -->
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style amp4email-boilerplate>body{visibility:hidden}</style>
<script async src="https://cdn.ampproject.org/v0.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
Hello, world.
</body>
</html>
Technically, this template will support AMP for email elements that only compatible clients will display. Other clients will still be able to render emails using regular HTML. In other words, you’d be creating two versions of each email you send out to your users. One email displaying AMP and the other using standard HTML. That is, of course, if you want to jump on the AMP bandwagon.
So far, Google has only confirmed support for a few AMP elements. Those include forms, selectors, lists, accordions, carousels, sidebars, light-boxes, images, and animations. Regular AMP supports more elements. However, these are some of the ones that Google has deemed secure for email environments. If you want to check out how your campaigns would translate to AMP, you can try out the AMP Playground using the project’s email template:
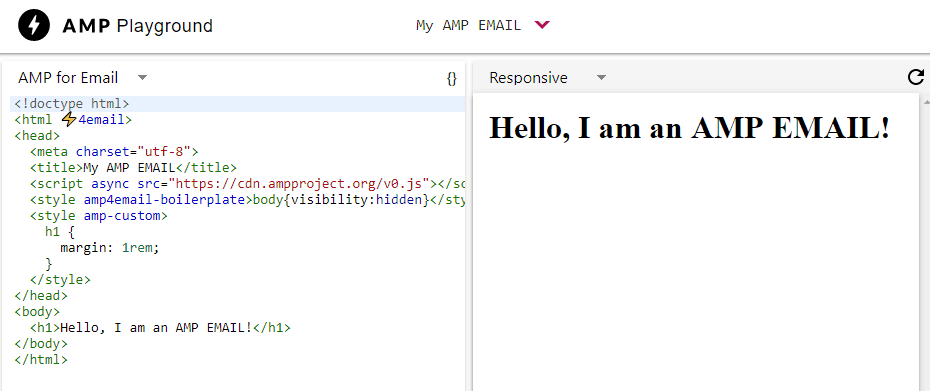
There, you’ll be able to test all the elements you want. This will give you a practical idea of what your campaigns could look like using AMP.
Conclusion
The AMP Project caused a stir when it launched in 2017. It’s still a controversial project, but it’s made some decent headway since its inception. More than 25 million domains have already started publishing AMP content, and Google are still increasing the project’s scope.
With AMP for email, Google managed to stir up even more feelings. Adding complex elements to email using a new framework may lead to compatibility issues, and AMP emails may even end up being less lightweight than their standard counterparts. Even so, you should take the time to prepare for what AMP for email may bring, as it’s sure to have an effect on your campaigns in the future.
What do you think about the Google AMP project and its expansion into email? Share your thoughts with us in the comments section below!
Article thumbnail image by Sammby / shutterstock.com
The post What We Know About Google AMP for Email (And How It May Affect Your Campaigns) appeared first on Elegant Themes Blog.
